Afar Region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Afar Region (; aa, Qafar Rakaakayak; am, አፋር ክልል), formerly known as Region 2, is a

 The continuous process of volcanism results in the occurrence of major
The continuous process of volcanism results in the occurrence of major
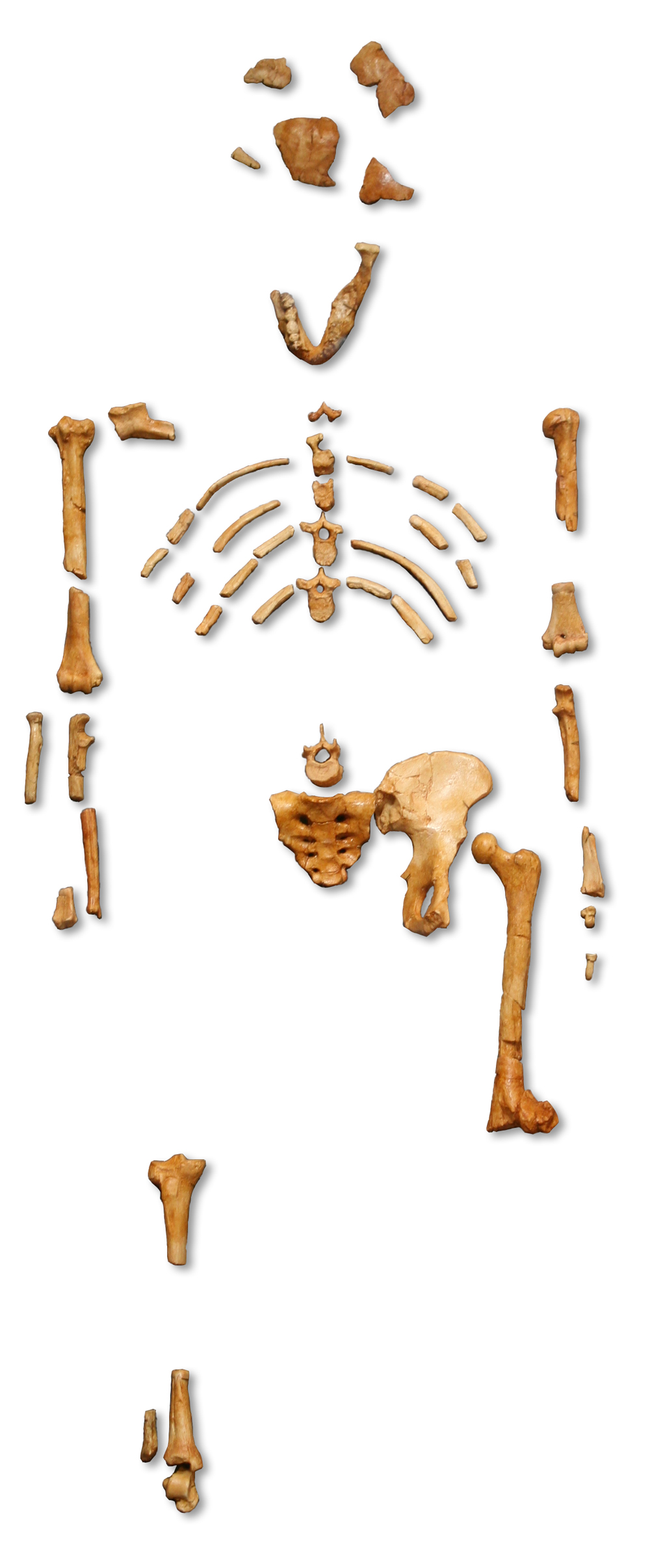 Hadar, a community in Afar, was the site of the discovery in 1973–74 of "
Hadar, a community in Afar, was the site of the discovery in 1973–74 of "
Worldstatesmen.org
)
Danakil depressionMap of Afar Region at DPPA of Ethiopia
(PDF file)
Afar TriangleLarge collection of photos from an expedition to the DanakilAfar Rift Consortium homepageInterview with Afar president, Ismael Ali Sirro
IRIN 24 May 2002 {{Authority control Regions of Ethiopia States and territories established in 1992
regional state
A regional state, or a regionalised unitary state, is a term used to denote a type of state that is formally unitary but where a high degree of political power has been highly decentralised to regional governments. This contrasts with a state org ...
in northeastern Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and the homeland of the Afar people
The Afar ( aa, Qafár), also known as the Danakil, Adali and Odali, are a Cushitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting the Horn of Africa. They primarily live in the Afar Region of Ethiopia and in northern Djibouti, as well as the entire southern co ...
. Its capital is the planned city of Semera
Samara ( aa, Samara; amh, ሰመራ) is the capital of Afar Region, Ethiopia. It is a town on the Awash–Assab highway in north-east Ethiopia, having been planned and built to replace Asaita. Located in Administrative Zone 1, Semara has a la ...
, which lies on the paved Awash– Assab highway.
The Afar Triangle
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; t ...
, the northern part of which is the Danakil Depression
The Danakil Depression is the northern part of the Afar Triangle or Afar Depression in Ethiopia, a geological depression that has resulted from the divergence of three tectonic plates in the Horn of Africa.
Geology
The Danakil Depression lie ...
, is part of the Great Rift Valley of Ethiopia, and is located in the north of the region. It has the lowest point in Ethiopia and one of the lowest in Africa. The southern part of the region consists of the valley of the Awash River
The Awash (sometimes spelled Awaash; Oromo: ''Awaash'', Amharic: አዋሽ, Afar: ''We'ayot'', Somali: ''Webiga Dir'') is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of i ...
, which empties into a string of lakes along the Ethiopian–Djibouti border. Other notable landmarks include the Awash National Park
Awash National Park is a national park in Ethiopia. Located at the border of Oromia state and Afar state, the park covers an area of 827 square kilometers, most of it lies at an altitude of 900 meters. Spanning across the southern tip of the ...
.
Demographics
Based on the 2017 projections by theCentral Statistical Agency
The Central Statistical Agency (CSA; Amharic: ማዕከላዊ ስታቲስቲክስ ኤጀንሲ) is an agency of the government of Ethiopia designated to provide all surveys and censuses for that country used to monitor economic and social growt ...
of Ethiopia (CSA), the Afar Regional State has a population of 1,812,002, consisting of 991,000 men and 821,002 women; urban inhabitants number 346,000 of the population, a further 1,466,000 were pastoralists.
Based on the 2007 Census conducted by the Central Statistical Agency
The Central Statistical Agency (CSA; Amharic: ማዕከላዊ ስታቲስቲክስ ኤጀንሲ) is an agency of the government of Ethiopia designated to provide all surveys and censuses for that country used to monitor economic and social growt ...
of Ethiopia (CSA), the Afar Regional State has a population of 1,390,273, consisting of 775,117 men and 615,156 women; urban inhabitants number 185,135 or 13.32% of the population, a further 409,123 or 29.43% were pastoralists
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The animal s ...
. With an estimated area of 96,707 square kilometers, this region has an estimated density of 14.38 people per square kilometer. For the entire region 247,255 households were counted, which results in an average for the Region of 5.6 persons to a household, with urban households having on average 4 and rural households 6 people.
In the previous census, conducted in 1994, the region's population was reported to be 1,106,383 of which 626,839 were men and 479,544 women; urban inhabitants were 85,879 or 7.76% of the population.
Afar is predominantly (89.96%) spoken in the region and is the working language of the state. Other languages with a significant number of speakers in the state include Amharic
Amharic ( or ; (Amharic: ), ', ) is an Ethiopian Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is spoken as a first language by the Amharas, and also serves as a lingua franca for all oth ...
(6.83%), Tigrinnya (1.06%), Argobba (0.79%), Wolaitta (0.43%), and Oromifa (0.4%).
According to the CSA, , 48.57% of the total population had access to safe drinking water, of whom 26.89% were rural inhabitants and 78.11% were urban. Values for other reported common indicators of the standard of living
Standard of living is the level of income, comforts and services available, generally applied to a society or location, rather than to an individual. Standard of living is relevant because it is considered to contribute to an individual's quality ...
for the Afar Regional State include the following: 67.3% of the inhabitants fall into the lowest wealth quintile; adult literacy for men is 27% and for women 15.6%; and the regional infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
is 61 infant deaths per 1,000 live births, which is less than the nationwide average of 77; at least half of these deaths occurred in the infants’ first month of life. On 20 April 2007, the regional government announced that it had increased health coverage from 34% to 40%, the result of construction of 64 new health clinics, increasing the total for the region to 111.
Land features

Afar Depression
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; th ...
, Erta Ale
Erta Ale (or Ertale or Irta'ale; Amharic: ኤርታሌ) is a continuously active basaltic shield volcano in the Afar Region of northeastern Ethiopia. It is situated in the Afar Depression, a barren desert area. Erta Ale is the most active volcano ...
active volcano, Awash National Park
Awash National Park is a national park in Ethiopia. Located at the border of Oromia state and Afar state, the park covers an area of 827 square kilometers, most of it lies at an altitude of 900 meters. Spanning across the southern tip of the ...
, Yangudi Rassa National Park
Yangudi Rassa National Park ( am, ያንጉዲ ራሳ ብሔራዊ ፓርክ, translit=yanigudī rasa biḥērawī pariki) is a national park in Ethiopia located in Afar Region.
Geography
Its of territory include Mount Yangudi () near the souther ...
, Hadar and Aramis
René d'Herblay, alias Aramis, is a fictional character in the novels ''The Three Musketeers'' (1844), '' Twenty Years After'' (1845), and '' The Vicomte de Bragelonne'' (1847-1850) by Alexandre Dumas, père. He and the other two musketeers, A ...
areas, are the major tourist attraction area of the region. The hot springs, Afar culture and cultural games are other attraction areas.
In 2005, a giant rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
was formed in just a few days. The rift opened when the Dabbahu Volcano
Dabbahu Volcano (also Boina, Boyna or Moina) is an active volcano located in the remote Afar Region of Ethiopia. This stratovolcano is part of the Afar Triangle (Afar Depression), a highly active volcanic region which includes Erta Ale. An erupti ...
, situated in the north of the region, erupted. The crack forming is thought to be part of the process in which the Arabian Plate
The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres.
It is one of the three continental plates (along with the African and the Indian Plates) that have been moving northward in geological history and collidin ...
and the two African plate
The African Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes much of the continent of Africa (except for its easternmost part) and the adjacent oceanic crust to the west and south. It is bounded by the North American Plate and South American Plate ...
s, the Nubian Plate and the Somali Plate, are moving apart. This new crack, long, and deep, opened when the lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
from the erupting volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
flowed underground and cooled forming a long, wide dike
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes ...
within days.
Environment
TheAfar Depression
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; th ...
, a plate tectonic triple junction, is found in the Afar Regional State. This geologic feature is one of Earth's great active volcanic areas. Due to this volcanic activity the floor of the depression is composed of lava, mostly basalt.
 The continuous process of volcanism results in the occurrence of major
The continuous process of volcanism results in the occurrence of major minerals
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2 ...
, including potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
, sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
, bentonite
Bentonite () is an absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelling capacity than Ca-mon ...
and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
. In addition to these minerals, there are also promising geothermal energy sources and hot springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
in different areas of the region. Most of the region's mineral potential are found in Dallol, Berhale
Berhale (also transliterated Berahle and Berahile) is a town in north-eastern Ethiopia. Located in Kilbet Rasu, Afar Region, this town has a latitude and longitude of with an altitude of 639 meters above sea level. It is the largest town in Berh ...
and Afdera woreda
Districts of Ethiopia, also called woredas ( am, ወረዳ; ''woreda''), are the third level of the administrative divisions of Ethiopia – after ''zones'' and the '' regional states''.
These districts are further subdivided into a number of ...
s of Zone Two. Elidar
Elidar is a town in north-eastern Ethiopia. Located in Administrative Zone 1 of the Afar Region, in the angle formed by the border with Djibouti to the south, and Eritrea to the northeast. It has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation ...
, Dubti
Dubti is a town in north-east Ethiopia. Located in Awsi Rasu, Afar Region, this town has a latitude and longitude of with an elevation of 378 meters above sea level.
A UN-EUE mission, accompanied by two non-government organizations, surveying co ...
and Millee in Zone One, and Gewane
Gewane is a town in north-eastern Ethiopia. Located in Administrative Zone 3 of the Afar Region, it has an elevation of 618 meters above sea level. Gewane is locally known as New Gewane, 2 kilometers east of the original settlement known as Old ...
in Zone Three, also have some mineral possibilities.
Afar is home to peculiar wild life, which notably include the African wild ass
The African wild ass (''Equus africanus'') or African wild donkey is a wild member of the horse family, Equidae. This species is thought to be the ancestor of the domestic donkey (''Equus asinus''), which is sometimes placed within the same spec ...
, Grevy's zebra, wild fox, wild cat, cheetah, and ostrich. These wild animals are found in the region's national parks. Because the region's tourism development is still in a poor state there are only two lodges in Awash National Park
Awash National Park is a national park in Ethiopia. Located at the border of Oromia state and Afar state, the park covers an area of 827 square kilometers, most of it lies at an altitude of 900 meters. Spanning across the southern tip of the ...
.
Agriculture
The CSA estimated in 2005 that farmers in the Afar Regional State had a total of 327,370 cattle (representing 0.84% of Ethiopia's total cattle), 196,390 sheep (1.13%), 483,780 goats (3.73%), 200 mules (0.14%), 12,270 asses (0.49%), 99,830 camels (21.85%), 38,320 poultry of all species (0.12%), and 810 beehives (less than 0.1%). The CSA estimated on the basis of a survey performed in December 2003 that nomadic inhabitants had 1,990,850 cattle (an 83.8% share of those animals in the region that year), 2,303,250 sheep (90.6%), 3,960,510 goats (90%), 759,750 camels (85.9%), 175,180 asses (92.5%), 2960 mules (88.6%), and 900 horses (100%).Regional instability
, the area has been increasingly unstable, as tensions between Ethiopia and Eritrea remain high after theEritrean–Ethiopian War
The Eritrean–Ethiopian War, also known as the Badme War, was a major armed conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea that took place from May 1998 to June 2000. The war has its origins in a territorial dispute between the two states. After Erit ...
of 1998 to 2000. On January 18, 2012, five foreign tourists were murdered while on holiday in the region. The Ethiopian government has accused Eritrean gunmen of being responsible for the attack. Many governments around the world advise against traveling to the Afar region, citing increasing security concerns.
Fossil finds
 Hadar, a community in Afar, was the site of the discovery in 1973–74 of "
Hadar, a community in Afar, was the site of the discovery in 1973–74 of "Lucy
Lucy is an English feminine given name derived from the Latin masculine given name Lucius with the meaning ''as of light'' (''born at dawn or daylight'', maybe also ''shiny'', or ''of light complexion''). Alternative spellings are Luci, Luce, Lu ...
", the ''Australopithecus afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not ...
'' skeletal remains, by Donald Johanson
Donald Carl Johanson (born June 28, 1943) is an American paleoanthropologist. He is known for discovering, with Yves Coppens and Maurice Taieb, the fossil of a female hominin australopithecine known as "Lucy" in the Afar Triangle region of Hada ...
of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History
The Cleveland Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum located approximately five miles (8 km) east of downtown Cleveland, Ohio in University Circle, a 550-acre (220 ha) concentration of educational, cultural and medical instit ...
. On March 5, 2005, another skeleton, estimated to be 3.8 million years old and said to be the world's oldest bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
hominid skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
, was found in the region. Yohannes Haile-Selassie
Yohannes Haile-Selassie Ambaye (born 23 February 1961) is an Ethiopian paleoanthropologist. An authority on pre-''Homo sapiens'' hominids, he particularly focuses his attention on the East African Rift and Middle Awash valleys.Mangels, John (200 ...
led digs there each year from 2004 to 2007.
On March 24, 2006, it was reported that a "significantly complete" cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
had been found at Gawis in the Gona area. The cranium appears as an intermediate form between ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'' and ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
''.
On October 1, 2009, scientists reported that they had found a skeleton, which dates around 4.4 million years ago. Named Ardi ARDI is the Access to Research for Development and Innovation program, a partnership between the World Intellectual Property Organization and major scientific and technical publishers. ARDI provides access to nearly 10,000 online journals, books and ...
, it is a form of the species ''Ardipithecus ramidus''. The specimen is a distant cousin of the ''Australopithecus afarensis'', Lucy's species.
In June 2010, the oldest direct evidence of stone tool manufacture was found in the Afar region and attributed to ''Australopithecus afarensis''.
In 2013, a graduate student from the Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public research university in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, ASU is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the ...
discovered a hominid jawbone in the Ledi-Geraru
Ledi-Geraru is a paleoanthropological research area in Mille district, Afar Region, northeastern Ethiopia, along the Ledi and Geraru rivers (two left tributaries of the Awash, south of the Mille river). It stretches for about 50 km, lo ...
region of Afar. Scientists estimated that the fossil dates back around 2.8 million years ago, which is 400,000 years before the next oldest hominid fossil remains.
In 2015, a hominin jawbone and teeth was discovered in the Afar region. Scientists believe that the bones belonged to a previously undiscovered ancestor. The new species was named "''Australopithecus deyiremeda''", meaning "close relative" in the native Afar language. The species lived around 3.5–3.3 million years ago, about the same time period as other hominins such as Australopithecus afarensis.
List of Chief Administrator of the Afar Region
*Habib Alimirah
Habib ( ar, حبيب, ''ḥabīb''; ), sometimes written as Habeeb, is an Arabic masculine given name, occasional surname, and honorific, with the meaning "beloved" or "my love", or "darling". It also forms the famous Arabic word ‘''Habibi’'' ...
( ALF) 1991? - 1995
* Hanfare Alimirah (ALF) September 1995 - Mar 1996
* Ismaqil Qali Siro ( APDO/ANDP) March 1996–September 2015
*Awol Arba Unde
Desertion is the abandonment of a military duty or post without permission (a pass, liberty or leave) and is done with the intention of not returning. This contrasts with unauthorized absence (UA) or absence without leave (AWOL ), which ar ...
(acting) September 2015 - November 2015
* Seyoum Awol (ANDP) 16 November 2015 - 16 December 2018
*Awol Arba Unde
Desertion is the abandonment of a military duty or post without permission (a pass, liberty or leave) and is done with the intention of not returning. This contrasts with unauthorized absence (UA) or absence without leave (AWOL ), which ar ...
(ANDP) 17 December 2018 – present
(This list is based on information froWorldstatesmen.org
)
Administrative zones
Like other regions in Ethiopia, Afar is subdivided into administrative zones (and one specialworeda
Districts of Ethiopia, also called woredas ( am, ወረዳ; ''woreda''), are the third level of the administrative divisions of Ethiopia – after ''zones'' and the '' regional states''.
These districts are further subdivided into a number of ...
, an administrative subdivision which is an autonomous area
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
and is not part of a zone).
*Awsi Rasu
Awsi Rasu, also known as Administrative Zone 1, is a zone in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. This zone is bordered on the south by Gabi Rasu, on the southwest by Hari Rasu, on the west by the Amhara Region, on the northwest by Fantí Rasu, on the ...
*Kilbet Rasu
Kilbatti (Kilbat) Rasu, also known as Administrative Zone 2, is one of the five zones in the Afar Region of Ethiopia. This zone is bordered on the south by Awsi Rasu, on the southwest by Fantí Rasu, on the west by the Tigray Region, and on the ...
* Gabi Rasu
* Fanti Rasu
* Hari Rasu
* Mahi Rasu
* Argobba (special woreda)
See also
*List of districts in the Afar region
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
*Regions of Ethiopia
Ethiopia is a federation subdivided into ethno-linguistically based regional states (Amharic: plural: ክልሎች ''kililoch''; singular: ክልል ''kilil''; Oromo: singular: ''Naannoo''; plural: ''Naannolee'') and chartered cities (Amharic: p ...
* Afar–Somali clashes
Notes and references
External links
Danakil depression
(PDF file)
Afar Triangle
IRIN 24 May 2002 {{Authority control Regions of Ethiopia States and territories established in 1992